Maple, Norway
Identification
Appearance
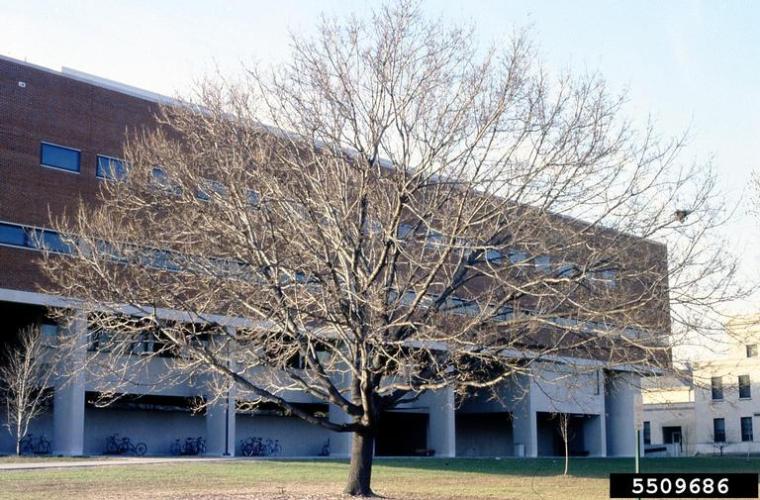
Acer platanoides is a tree that usually grows to 40-60 feet in height, but can reach heights of 100 feet. The bark of the tree is grayish and regularly and shallowly grooved.
Foliage
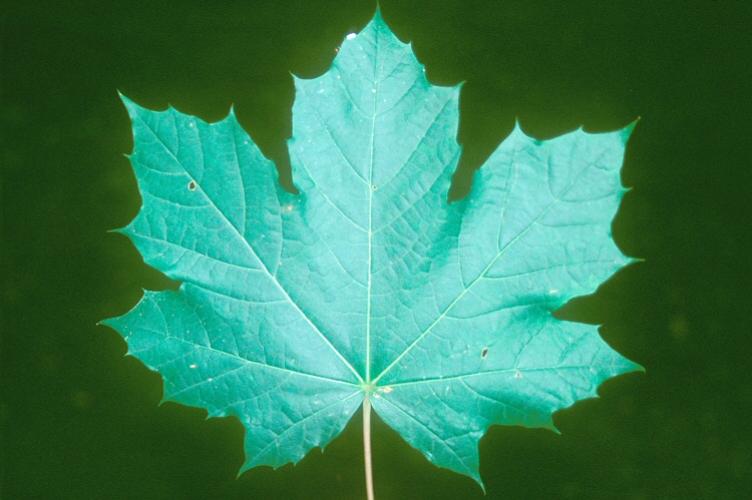
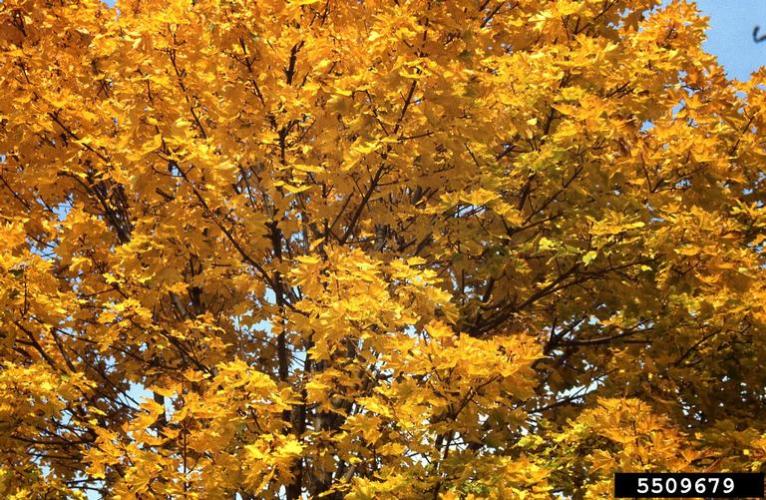
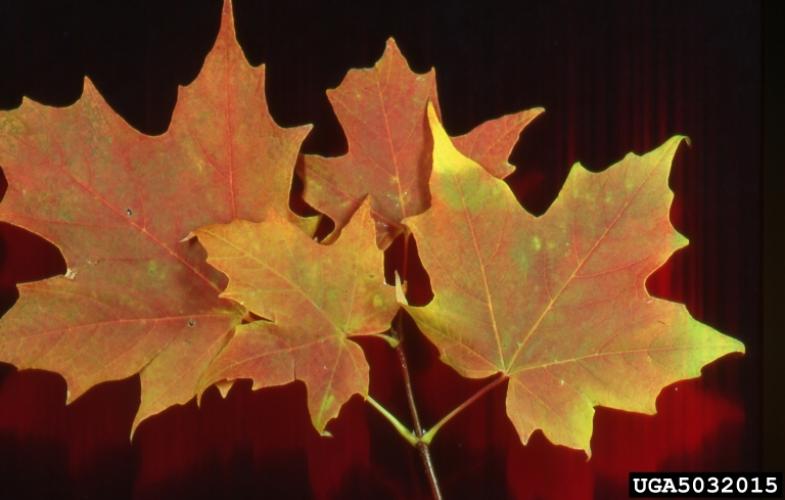
The palmately lobed leaves are opposite and have 5 to 7 sharply acuminate lobes (with large but few teeth). These leaves are 4-7 inches wide. The leaf petioles exude a white sap when broken. The leaves are usually green in color, but there are some cultivars that have dark red leaves. The fall color of the green leaves is yellow.
Flowers
The flowers appear in April and May and are yellow-green in color. They are borne in erect, pedunculate, rounded corymbs. Each flower is 0.25 inches wide.
Fruit
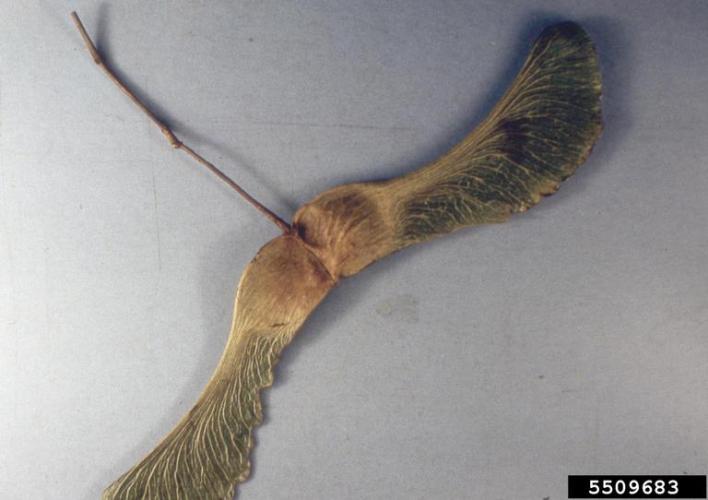
The pendulous fruit measure 1.5-2 inches in length. The fruit are samaras that are green when young and turn yellow, then brown, with age. The samara wings are divergent, reaching nearly 180 degree angle to each other and are dispersed by wind.
Biology
This species is Quarantined: Class B Noxious Weed
Origin
Native to Europe and Asia, Norway maple was first introduced to the United States by the famous Pennsylvania botanist, John Bartram, in 1756. It was seen as a very popular street tree because of its hardiness. However, it has readily spread through New England forests and is now regarded as an invasive species, capable of shading out native trees.
Habitat
Man-made or disturbed sites, forest edges, and forests.
Life Cycle
The yellowish-green flowers of Norway maple appear in stalked clusters in mid to late April as the leaves are expanding. They are insect pollinated. Fruits mature in late summer into wide-spreading wings that split down the middle. Large numbers of shade-tolerant seedlings are produced. Populations of these trees will also expand locally by vegetative reproduction.
ecological threat
- Unlike native tree species, Norway maple hosts very few native caterpillars, reducing an important food source for bird populations
- Native mammals do not recognize Norway maple seeds as a food source, further reducing native tree populations.
- Norway maple (Acer platanoides) provides breeding habitat for another highly invasive species, the Asian longhorned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis), an insect that threatens to significantly reduce North American hardwood forest stands. Research shows female beetles will live longer and produce more fertile eggs on non-native Norway maples than on native red maples (Acer rubrum).
Vermont Distribution
Citations
Photo credit
Norway maple leaf, 5391792, John M. Randall, The Nature Conservancy, Bugwood.org
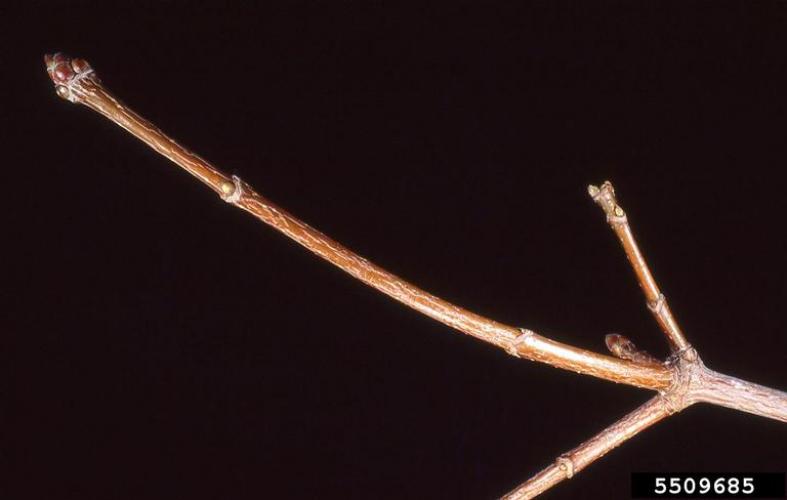
Norway maple twig, 5509685, T. Davis Sydnor, The Ohio State University, Bugwood.org
Norway maple tree form, 5509686, T. Davis Sydnor, The Ohio State University, Bugwood.org
Norway maple bark, 5499602, David Stephens, Bugwood.org
Fruit (samara), 5509683, T. Davis Sydnor, The Ohio State University, Bugwood.org
Fall foliage, 5509679, T. Davis Sydnor, The Ohio State University, Bugwood.org
Sugar maple, 5032015, Joseph OBrien, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
information credit
Center for Invasive Species and Ecosystem Health, Norway Maple
University of Minnesota Extension